
Mathematics-Online course: Preparatory Course Mathematics - Basics - Propositional Logic
|
[home] [lexicon] [problems] [tests] [courses] [auxiliaries] [notes] [staff] |

|
|
Mathematics-Online course: Preparatory Course Mathematics - Basics - Propositional Logic | ||
Logical Compositions | ||
| [previous page] [next page] | [table of contents][page overview] |
| Operation | Notation | (read as) | is true if and only if | ||||||||
| Negation | (not |
||||||||||
| Conjunction | ( |
both |
|||||||||
| Disjunction | ( |
||||||||||
| Antivalence |
|
(either |
|||||||||
| Implication |
|
|
|||||||||
| Equivalence |
|
( |
In order to reduce the usage of parentheses in logical formulas, we define that ![]() is more closely linked to a symbol than
is more closely linked to a symbol than ![]() and
and ![]() , which in turn are more closely linked than
, which in turn are more closely linked than
![]() ,
,
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
Note that an implication
![]() only requires the truth of
only requires the truth of ![]() if
if ![]() is true.
A false proposition implies anything, hence both true and false implications can be drawn.
is true.
A false proposition implies anything, hence both true and false implications can be drawn.
Usually, the or-connective is symbolised by a v, derived from the word vel (Latin: or), yet it is also
common practice
to use the symbol ,,![]() ``; then ,,
``; then ,,![]() ``symbolizes the and-connective. Using 0 to refer to the truth value ,,false``while interpreting any other value as ,,true``enables us to determine the truth value of logical formulas via calculation with natural numbers.
``symbolizes the and-connective. Using 0 to refer to the truth value ,,false``while interpreting any other value as ,,true``enables us to determine the truth value of logical formulas via calculation with natural numbers.
Particularly computer-linguists frequently use the English terms NOT (negation), AND (conjunction), OR (disjunction), EXOR or XOR (exclusive or, antivalence) as well as their negations NAND (negated conjunction), NOR (negated disjunction) and NXOR (equivalence).
| and-connective | or-connective |
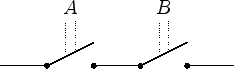 |
![\includegraphics[origin=tl]{logische_schaltungen_oder}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img2.png) |
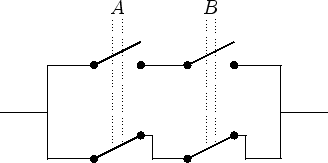
A negated statement corresponds to a switch that is closed if the statement is false. Thus it is possible to draw circuits representing equivalence, antivalence and implication.
| Equivalence:
|
 |
| Antivalence:
|
![\includegraphics[origin=tl]{logische_schaltungen_ungleich}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img10.png) |
| Implication:
|
![\includegraphics[origin=tl]{logische_schaltungen_implikation}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img11.png) |
Switches can be represented by transistors, for example, that conduct electricity when a high or low voltage is impressed. Values w and f (or 1 and 0) represent high and low voltages respectively.
DIN 40900 defines symbols for the corresponding circuits. These consist of rectangles in which the respective operations are inscribed. Negation is symbolized by a circle.
| Conjunction | Disjunction | Antivalence |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_und}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img12.png) |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_oder}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img13.png) |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_exor}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img14.png) |
| Negation | Implication | Equivalence |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_not}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img15.png) |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_implikation}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img16.png) |
![\includegraphics[width=0.25\moimagesize]{din_gleich}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel983/img17.png) |
| [previous page] [next page] | [table of contents][page overview] |
| automatically generated 1/9/2017 |