
Mathematics-Online course: Linear Algebra - Matrices - Special Matrices
|
[home] [lexicon] [problems] [tests] [courses] [auxiliaries] [notes] [staff] |

|
|
Mathematics-Online course: Linear Algebra - Matrices - Special Matrices | ||
Fourier Matrices | ||
| [previous page] [next page] | [table of contents][page overview] |
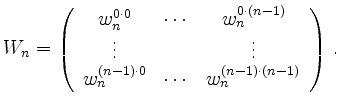
| automatically generated 4/21/2005 |