
Mathematics-Online lexicon:
|
[home] [lexicon] [problems] [tests] [courses] [auxiliaries] [notes] [staff] |

|
|
Mathematics-Online lexicon: | ||
Linear Approximation of Functions of Several Variables | ||
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | overview |
To stress the limit process
![]() one often writes
one often writes
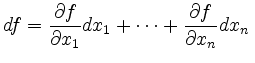
with differentials ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The linear function
is called the linear approximation of ![]() at
at ![]()
If
![]() is a scalar function of three variables
is a scalar function of three variables ![]() and
and ![]() , then
the linear approximation at
, then
the linear approximation at
![]() is given by
is given by
see also:
| automatically generated 8/ 4/2008 |